Wrongfully Convicted African-Americans Wait Longer To Be Exonerated Than Others: Study
/
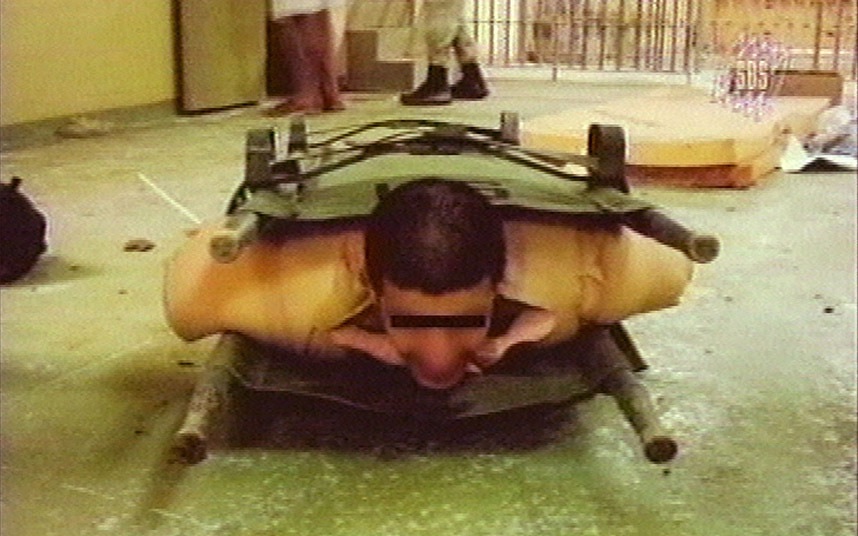
It took 18 years for DNA evidence to surface that cleared Derrick Williams of a rape and attempted kidnapping in Florida. Prosecutors had relied on the testimony of the victim, who identified Williams as her attacker in 1992. But he walked free at age 48 in 2011 because his DNA didn't match that left on a gray T-shirt by the actual perpetrator.
The truth might have surfaced sooner if Williams were white or Latino instead of African-American.
There's no way to know for sure, of course, but data about wrongful convictions show that blacks who are exonerated after a bogus conviction have served 12.68 years on average before the good news, according to Pamela Perez, professor of biostatistics at Loma Linda University. It takes just 9.4 years for whites and 7.87 for Latinos.
"Black Americans are exonerated at a substantially slower rate than any other race," said a new report from Perez, shown exclusively to The Huffington Post.
There's enough of a pattern that the differences between racial groups cannot be called random, Perez said. But there isn't enough information to explain what caused the differences.
"All we can do is infer," Perez told HuffPost. "You can't prove a darn thing."
She discovered the different timespans by examining 1,450 exonerations listed on the National Registry of Exonerations through Oct. 20, 2014. Perez conducted the research for Safer-America.com, a consumer research group.
Safer-America translated the data into a map showing exoneration information across the U.S.