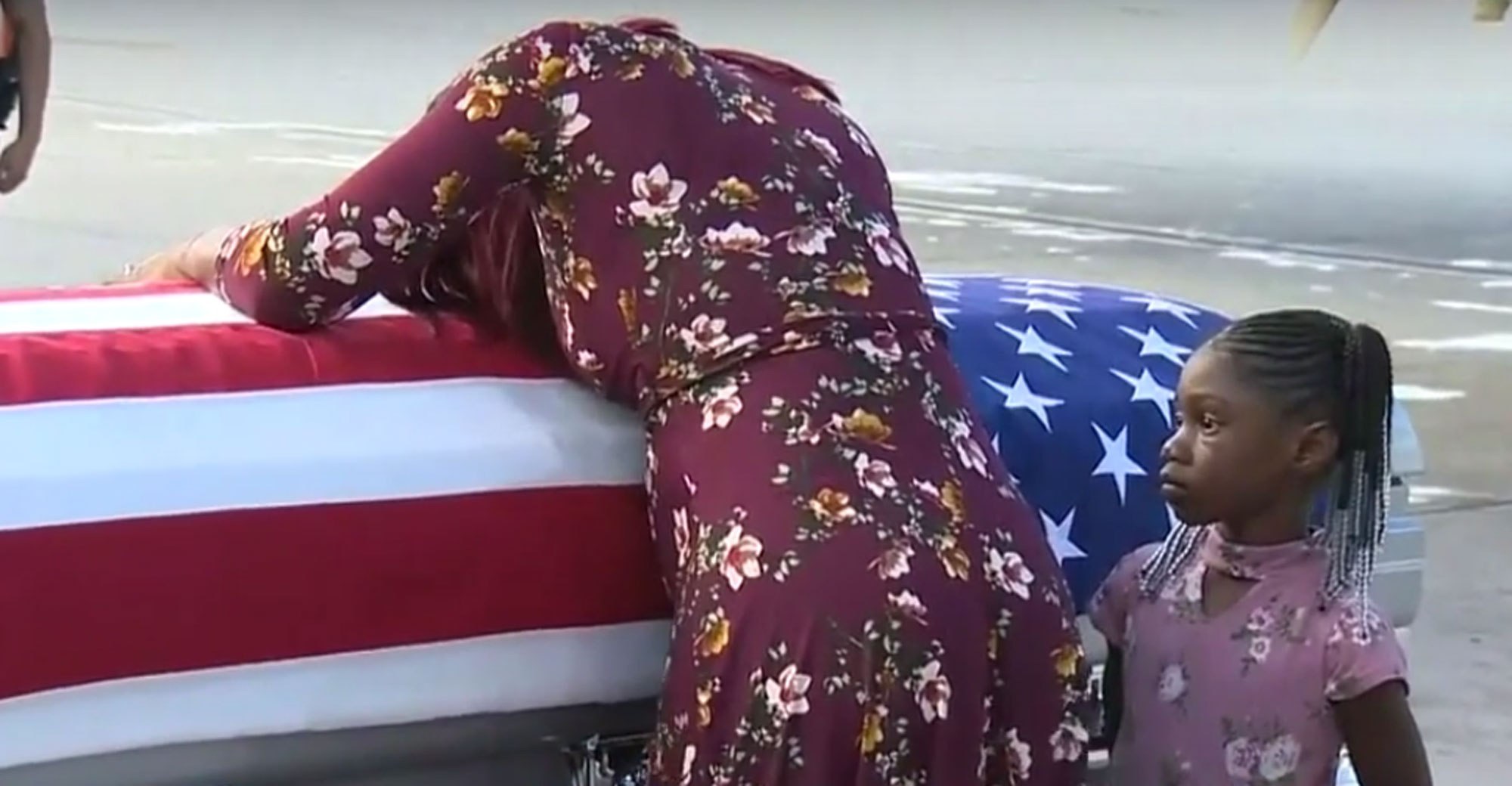
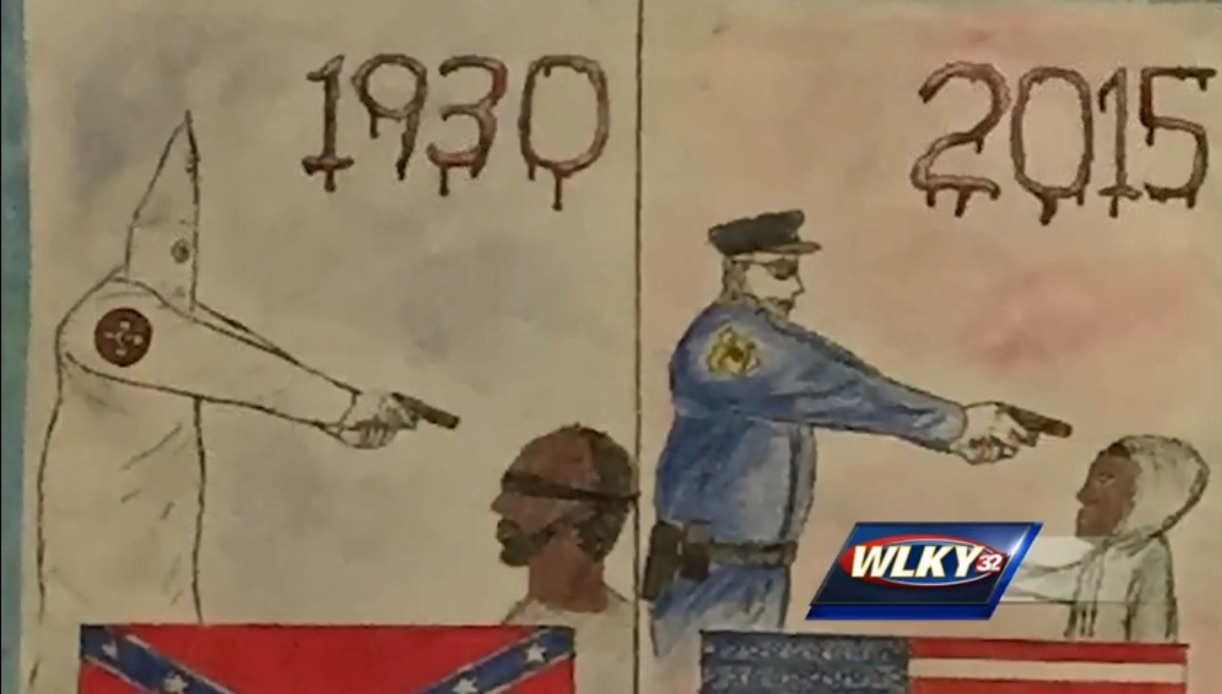
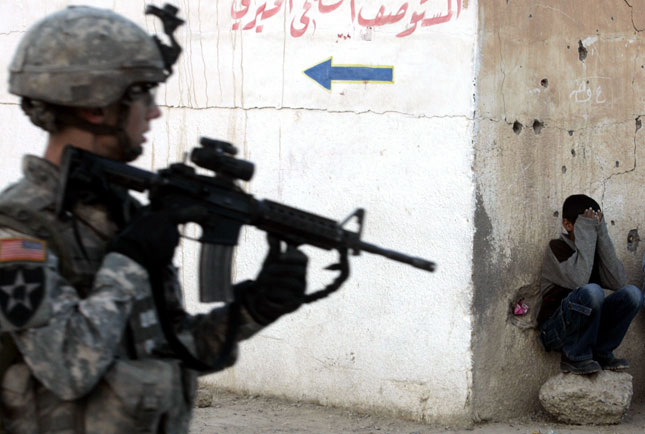
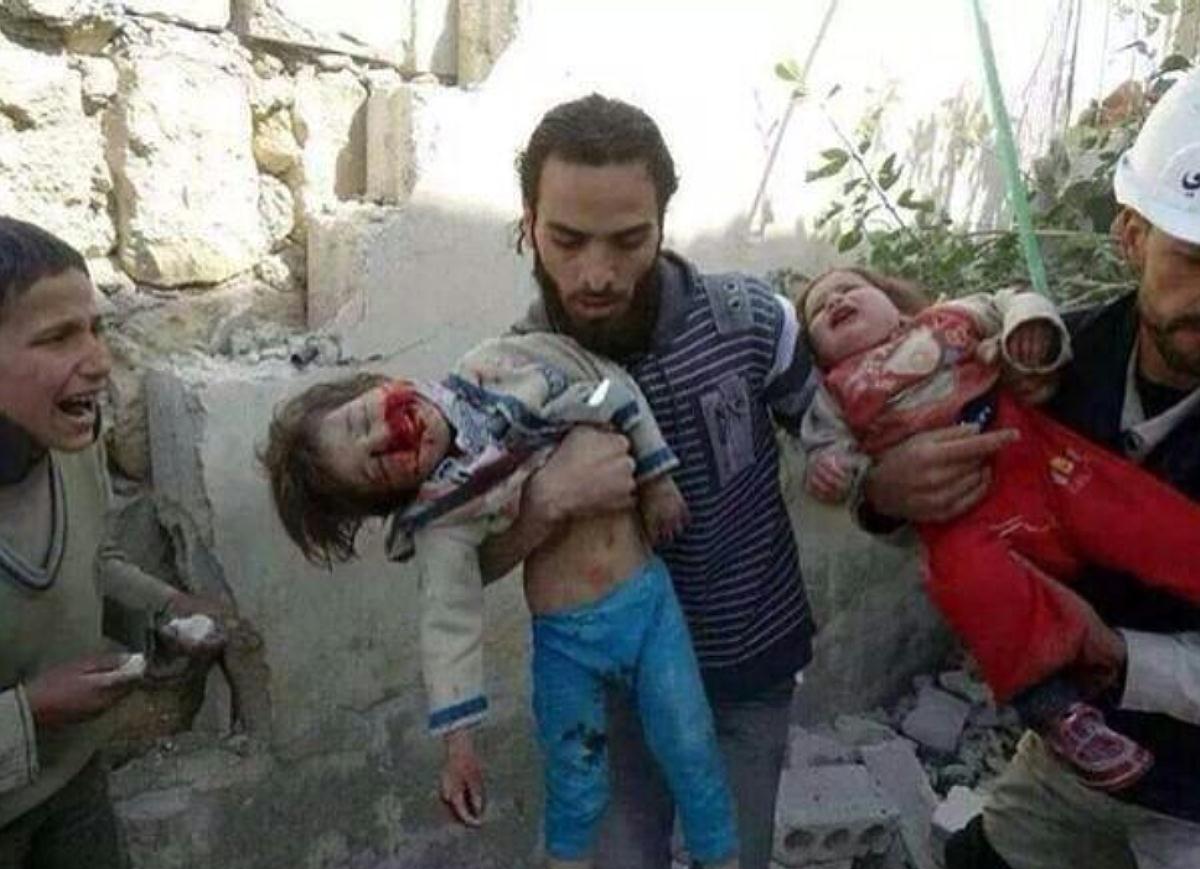
Study: All-White Jury Pools Convict Black Defendants 16 Percent More Often Than Whites
/Juries formed from all-white jury pools in Florida convicted black defendants 16 percent more often than white defendants, a gap that was nearly eliminated when at least one member of the jury pool was black, according to a Duke University-led study.
The researchers examined more than 700 non-capital felony criminal cases in Sarasota and Lake counties from 2000-2010 and looked at the effects of the age, race and gender of jury pools on conviction rates.
The jury pool typically consisted of 27 members selected from eligible residents in the two counties. From this group, attorneys chose six seated jurors plus alternates.
"I think this is the first strong and convincing evidence that the racial composition of the jury pool actually has a major effect on trial outcomes," said senior author Patrick Bayer, chairman of Duke's Economics Department.
"Our Sixth Amendment right to a trial by a fair and impartial jury of our peers is a bedrock of the criminal justice system in the U.S., and yet, despite the importance of that right, there's been very little systematic analysis of how the composition of juries actually affects trial outcomes, how the rules that we have in place for selecting juries impact those outcomes," Bayer said.
The study, posted Tuesday on the Quarterly Journal of Economics (http://www.oxfordjournals.org/page/4595/1), focused on how conviction rates varied with the composition of the jury pool, which is randomly determined by which eligible residents are called for jury duty that day.