Where the U.S. imports its oil from, in one map
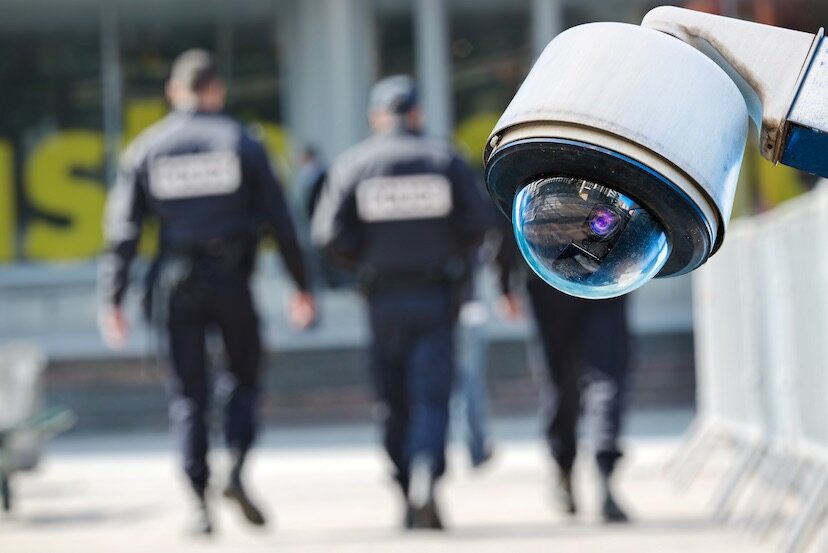
/The United States imported about 40 percent of its oil in 2012. So where are we getting it from? It depends a lot on where you live. Over at Business Insider, Rob Wile digs up this fascinating map from RBC Capital Markets:

For refineries on the East Coast, the majority of their imported oil comes from Africa, mainly Nigeria and Angola. By contrast, refineries in the Midwest get virtually all of their imported oil via pipeline from Canada.
Also note that relatively little of America’s imported crude comes from the Middle East, with the bulk of that (about 1.1 million barrels per day) getting shipped in through ports to refineries in the South, with much of the resulting gasoline and diesel getting shipped up to the Midwest. (For more detail on the different districts and how they exchange fuel, see here.)
Now what will happen in the years ahead, as the United States ramps up its domestic oil production, thanks to new drilling in places like North Dakota and Texas? Remember, the Energy Information Administration now expects U.S. oil imports to shrink from 8.3 million barrels per day down to 6 million barrels per day by the start of 2014.
That’s where things get tricky. The United States won’t simply be able to keep buying from the countries we like and shut off imports from countries we don’t like. As a recent investigation from Bloomberg’s Matthew Philips detailed, the changes will be a lot messier than that.
Over the past few years, U.S. refineries in the Midwest and elsewhere have spent billions upgrading their facilities in order to be able to process heavy, sour crude—the stuff that comes from the tar sands of Canada, or from Venezuela and Mexico. In order to recoup their investment, those refineries are likely to continue importing heavy oil from those three countries in the years ahead.
By contrast, the light, sweet crude that’s now pouring out of shale formations in North Dakota and Texas will mainly displace oil from Africa:
Since July 2010, the U.S. has cut its Nigerian imports by half, from more than 1 million barrels a day, to 543,000 as of October 2012, the most recent data available through the EIA. Imports from Angola have dipped below 200,000 daily barrels, from an average of 513,000 in 2008.
“By the second quarter of this year, we will stop importing West African light, sweet crude into the Gulf,” Morse predicts. Those barrels will have to find another home, more than likely India, China, Europe, and Korea. [MORE]